Polyacrylamide (PAM)
CAS No.:
9003-05-8
Molecular Formula:
(C3H5NO)n
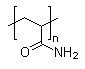
Structure Formula:
Properties:
Polyacrylamide, abbreviation PAM, is a glassy solid, apt to water absorption. Polyacrylamide is the speed of absorbing water that varies with different derivative ions.
Polyacrylamide could be made into four series: no-ion, cation, anion, and mixed cation&anion.
Specifications:
| Item | Powder (No-ion) | Powder (Anion) | Powder (Cation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White or light Yellow particle | White or light Yellow particle | White or light Yellow particle |
| Solid Content, % | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 |
| Molecular Weight | As per requirement | As per requirement | As per requirement |
| Free Substance, % | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Time for Water-Soluble | 2h Max. | 2h Max. | 2h Max. |
| Hydrolysis Rate | As per requirement | As per requirement | Cation Rate:As per requirement |
| Item | Colloid (No-ion) | Colloid (Anion) | Colloid (Cation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White colloid | White colloid | White colloid |
| Solid Content, % | 8-30 | 8-30 | 8-30 |
| Molecular Weight | As per requirement | As per requirement | As per requirement |
| Free Substance, % | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Time for Water-Soluble | 2h Max. | 2h Max. | 2h Max. |
| Hydrolysis Rate | As per requirement | Cation Rate: As per requirement | As per requirement |
Uses:
Polyacrylamide is an important water-soluble compound with flocculation properties, thickening, cut-resisting, block-reducing dispersing, etc.
Polyacrylamide properties vary with different derivative ions. So polyacrylamide is widely used in oil extraction, mining selection, coat washing, metallurgy, chemical, papermaking, sugar refining, pharmaceutical, environment protection, construction materials, and agriculture.
Packing and Storage:
25 kg/bag(Powder), 25 kg/bag(Colloid), the inner bag is PVC film, and the outer weaved plastic bags.
Keep dry.
Synonyms:
Polyacrylamide, PAM, PHPA.