2-Acrylamido-2-Methylpropane Sulfonic Acid (AMPS)
CAS No.:
15214-89-8
Molecular Formula:
C7H13NO4S
Molecular Weight:
207.25
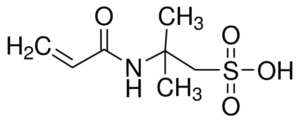
Structure Formula:
Properties:
2-Acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS) is a sulfonic acid acrylic monomer. It is reactive and hydrophilic. The sulfonate group gives the monomer a high degree of hydrophilicity and anionic character at a wide pH range. AMPS absorbs water readily and imparts enhanced water absorption and transport characteristics to polymers.
2-Acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid changes the chemical properties of a wide variety of anionic polymers. AMPS is very soluble in water and dimethylformamide (DMF) and shows limited solubility in most polar organic solvents.
Specifications:
| Items | Index |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White solution |
| Melting point | 195-200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 1.45 |
| Vapor Pressure, (25 °C) | <0.0000004 hPa |
| Flash point | 160 °C |
| pka | 1.67±0.50 (Predicted) |
| Water Solubility, (20 ºC) | 1500g/L |
| Solubility | >500g/L |
Uses:
1. Water treatment applications.
The cation stability of the AMPS-containing polymers is very useful for water treatment processes. Such polymers with low molecular weights can inhibit calcium, magnesium, and silica scale in cooling towers and boilers and help corrosion control by dispersing iron oxide. When high molecular weight polymers are used, they can precipitate solids in the treatment of industrial effluent stream.
2. Oil field applications.
Polymers in oil field applications must stand in hostile environments and require thermal and hydrolytic stability and resistance to hard water-containing metal ions. For example, in drilling operations where high salinity, high temperature, and high pressure are present, AMPS copolymers can inhibit fluid loss and be used in oil field environments as scale inhibitors, friction reducers, and water-control polymers and in polymer flooding applications.
3. Construction applications.
Superplasticizers with AMPS are used to reduce water in concrete formulations. The benefits of these additives include improved strength, workability, and durability of cement mixtures. In addition, re-dispersible polymer powder, when AMPS is introduced in cement mixtures, controls air pore content and prevents agglomeration of powders during the spray-drying process from powder manufacturing and storage.
Coating formulations with AMPS-containing polymers prevent calcium ions from forming as lime on the concrete surface and improve the appearance and durability of the coating.
4. Medical hydrogel applications.
High water-absorbing and swelling capacity when introducing AMPS to a hydrogel are keys to medical applications. In addition, Hydrogel with AMPS showed uniform conductivity, low electrical impedance, cohesive strength, appropriate skin adhesion, and biocompatible and capable of repeated use and have been used for electrocardiograph (ECG) electrodes, defibrillation electrode, electrosurgical grounding pads, and iontophoretic drug delivery electrodes.
In addition, polymers derived from AMPS are used as the absorbing hydrogel and the tackifier component of wound dressings. Finally, it is used due to its high water absorption and retention capability as a monomer in superabsorbent, e. g. for baby diapers.
5. Personal care products.
Strong polar and hydrophilic properties introduced to a high molecular weight AMPS homopolymer are exploited as a very efficient lubricant characteristic for skin care.
6. Coating and adhesive.
Its sulfonic acid group gives the monomers ionic character over a wide pH range. Anionic charges from AMPS fixed on polymer particles enhance the chemical and shear stabilities of polymer emulsion and reduce surfactants leaching out of paint film. It improves adhesive thermal and mechanical properties and increases pressure-sensitive adhesive formulations’ adhesive strength.
7. Detergents.
Enhances the washing performance of surfactants by binding multivalent cations and reducing dirt attachment.